
Incandescent

Compact fluorescent
Led

Led 101
The led difference explained
Let’s compare the 3 main light sources on the market.

Incandescent
Incandescent bulbs contain a filament that is heated up until it emits light.
FACTS
1.
Filaments in incandescent bulbs are fragile and burn out or break relatively easily.
2.
Governments around the world have passed measures to phase out incandescent light bulbs for general lighting by 2015.
20%
efficiency
80% wasted power

Compact fluorescent
Compact Fluorescent Lights (CFL) generate light by a high voltage arc passing through mercury vapor. The arc generates high energy ultraviolet light that is absorbed by a phosphor coating inside the lamp, which causes it to glow.
FACTS
1.
Although energy efficient, CFLs contain mercury, which presents disposal issues and environmental concerns.
Looong
warm
up
time
flickering
+ color variation

Led
LEDs are semiconductors (materials that transport an electrical charge). They produce light when an electrical current passes through them.
FACTS
1.
They produce light very efficiently, requiring considerably less watts than traditional lights.
2.
Average life span of LEDs is between 25,000 and 40,000 hours.
90%
efficiency
less heat
more power
Lumen
A Lumen (Lm) is the unit used to measure the brightness of a light source. The higher the Lumens, the brighter the light.
Lumens are best way to determine whether a bulb will provide you with the brightness you are looking for.
The new way to shop for light bulbs!
 vs
vs



The beam angle
Beam Angle is a light source's measure of light distribution and is particularly useful
to know when figuring out how well lit a specific area needs to be.
Narrow flood
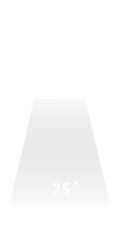
A precise and focused beam of light
Often used to highlight a specific feature (art)
Flood multi-purpose

A medium-sized beam of light
Often used for general-purpose lighting
Wide flood multi-purpose
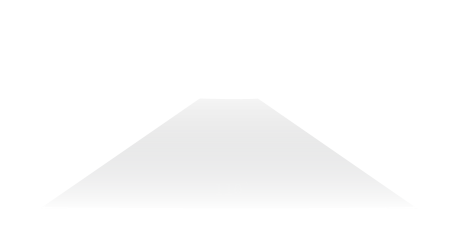
A wide and dispersed beam of light
Often used for general-purpose lighting
Omnidirectional

Distributes light
in all directions.
The color of light
The Correlated Colour Temperature (CCT) is measured in Kelvin (K)
and defines whether a light appears
Warm
Soothing, perfect for residential settings. Similar to light produced by an incandescent bulb.
Neutral
Bright, suitable for highlighting specific features or general residential settings. Similar to the light produced by a halogen bulb.
Cold
Stronger, cooler suitable for commercial and office settings. Similar to the light produced by a Compact Fluorescent bulb.
The led words
Watts
A Watt (W) is a measurement of how fast a bulb consumes energy. With incandescent bulbs, consumers equated WATTS with BRIGHTNESS. This is, in fact, wrong. The reason that this association became the norm was that in order for incandescent bulbs to reach elevated brightness, they required high power consumption or WATTS. LEDs use significantly less WATTS to produce the same quality of light that we are used to.
Efficiency
Efficiency measures how effective a bulb is at transforming the power used to run it (WATTS) into light output (Lumens). The higher the Efficiency, the more efficient your bulb is. Efficiency = Lumens / Watts
Dimmable
Dimmable bulbs can be adjusted to varying levels of brightness using a dimmer switch. Not all LED bulbs are dimmable.
Energy star®
ENERGY STAR® is an internationally recognized certification that is only given to products that meet strict energy efficiency standards. A product that is ENERGY STAR® CERTIFIED typically rates in the top 15 to 30 percent of its class for energy performance.
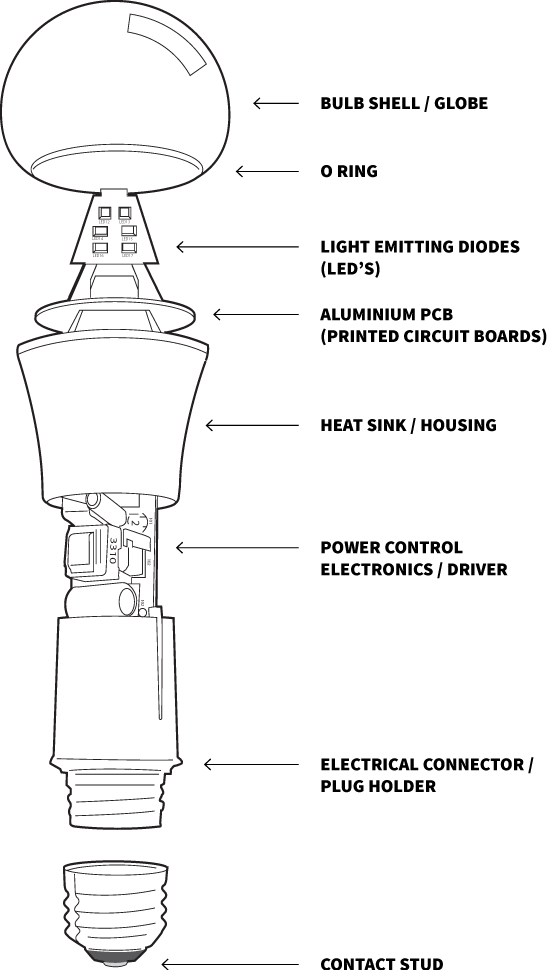
Key benefits

Shock resistance

Longevity

Consumption & Efficiency

Eco responsible choice
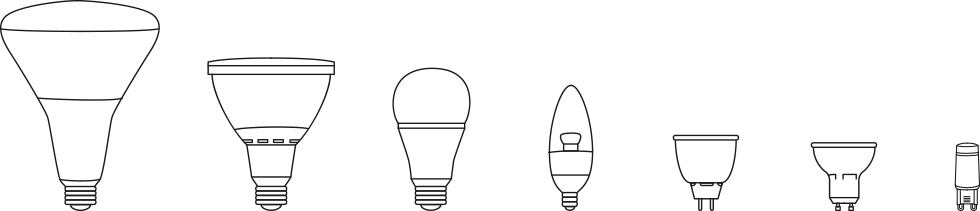
Flexibility
Led bulbs can be used to replace all bulb shapes, unlike compact fluorescent bulbs